Source: https://bigthink.com/strange-maps/baltic-odyssey/
Archive: https://archive.ph/YuKbh
Freezing cold, night battles, and a wrong-sized Hellespont: all clues that Ulysses sailed the Baltic instead of the Mediterranean.
Key Takeaways
Had he not wrapped himself in a discarded cloak, Ulysses would have frozen to death at Troy. Our hero’s host, Eumaeus the swineherd, hears the story and gets the hint: He loans Ulysses a cloak, because again, the night is freezing cold.
This part of Homer’s Odyssey doesn’t sound very Mediterranean. Sprinkled through Homer’s twin epics, Felice Vinci spotted a heap of similar anecdotes that pointed away from the traditional setting of the Iliad, an account of the Trojan War, and the Odyssey, the story of Ulysses’ 10-year journey home to Ithaca after the fall of Troy.
For Vinci, a nuclear engineer by training and an amateur historian by passion, the clues added up to a shocking revelation: Those Homeric stories, cornerstones of ancient Greek and modern Western culture, do not take place in and around Greece, in southern Europe, but rather near the Baltic Sea, in northern Europe.
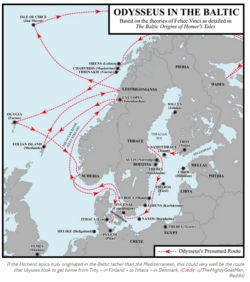
If that’s true, the Trojan War was a Nordic conflict and the Odyssey was a Baltic adventure. Vinci obliges, by matching key places in the epic stories to locations in northern Europe. As the map shows, the “ringing plains of Troy” would have been situated in southern Finland.
And it’s not just that starting point of the Odyssey that is outlandish; the other stops along the way are equally strange. Vinci identifies the location of the Greek city of Thebes with that of the Swedish capital of Stockholm. Hellas — the classical name for Greece — is in Estonia, while northern Poland is Egypt (and the location of the Egyptian city of Thebes).
Illustrious Athens once stood where the southern Swedish town of Karlskrona now rears its roofs: charming and baroque, but definitely less grand and much more recent. Copenhagen is Mycenae, while Ogygia, the island where the nymph Calpyso held Ulysses captive for seven years, is one of the Faroe Islands.
The cyclopes lived in Norway’s Tosenfjorden. Hades, the pagan Greek underworld, was in Russian Karelia. And Ithaca, the mythical home of Ulysses, is the tiny and otherwise rather unremarkable Danish island of Lyø.
Still, Vinci is not alone. The identity of Ithaca, so vaguely described by Homer, continues to exercise writers and historians. Some examples from recent centuries:
Archive: https://archive.ph/YuKbh
Was the “Odyssey” originally set in the Baltic?
The Trojan War was fought in Finland and Ulysses sailed home to Denmark, says one controversial theory.Freezing cold, night battles, and a wrong-sized Hellespont: all clues that Ulysses sailed the Baltic instead of the Mediterranean.
Key Takeaways
- The Iliad and Odyssey, Homer’s twin epics, seem to contain signature details suggesting these stories took place in particular settings.
- Where? Not the Mediterranean but the Baltic, writes an Italian amateur historian.
- So, is mythical Ithaca really the Danish island of Lyø? Other explanations are available.

Had he not wrapped himself in a discarded cloak, Ulysses would have frozen to death at Troy. Our hero’s host, Eumaeus the swineherd, hears the story and gets the hint: He loans Ulysses a cloak, because again, the night is freezing cold.
This part of Homer’s Odyssey doesn’t sound very Mediterranean. Sprinkled through Homer’s twin epics, Felice Vinci spotted a heap of similar anecdotes that pointed away from the traditional setting of the Iliad, an account of the Trojan War, and the Odyssey, the story of Ulysses’ 10-year journey home to Ithaca after the fall of Troy.
For Vinci, a nuclear engineer by training and an amateur historian by passion, the clues added up to a shocking revelation: Those Homeric stories, cornerstones of ancient Greek and modern Western culture, do not take place in and around Greece, in southern Europe, but rather near the Baltic Sea, in northern Europe.
Extraordinary claims, extraordinary proof
Extraordinary claims require extraordinary proof, and Vinci produces some compelling pieces of evidence. In his 1995 book Omero nel Baltico (translated as The Baltic Origins of Homer’s Epics), he points to:- numerous climate anomalies in Homer’s works, for example cool, foggy weather and snow dusting the shields of the warriors
- various geographic discrepancies, such as references to the “wide Hellespont,” which would fit better with the broad Gulf of Finland
- several topographic correspondences — for example, Troy could be the southern Finnish town of Toijala, Chios the Estonian island of Hiiumaa, and Pylene the northern German town of Plön
- reports of fighting at night, which would be possible thanks to long summer days in northern latitudes
- the boats in the Odyssey having two prows so they can be pointed in either direction, just like typical Viking longships
The Dorian invasion (oral epics included)
When the climate cooled, that civilization migrated south, to Greece. This would be the so-called Dorian invasion, with newcomers from the north taking over from the pre-classical inhabitants of Greece. Those Dorians brought from the north their culture, including northern original place names that were recycled for use in the eastern Mediterranean, as well as the orally transmitted epics that would be refashioned into the Iliad and Odyssey.If that’s true, the Trojan War was a Nordic conflict and the Odyssey was a Baltic adventure. Vinci obliges, by matching key places in the epic stories to locations in northern Europe. As the map shows, the “ringing plains of Troy” would have been situated in southern Finland.
And it’s not just that starting point of the Odyssey that is outlandish; the other stops along the way are equally strange. Vinci identifies the location of the Greek city of Thebes with that of the Swedish capital of Stockholm. Hellas — the classical name for Greece — is in Estonia, while northern Poland is Egypt (and the location of the Egyptian city of Thebes).
Illustrious Athens once stood where the southern Swedish town of Karlskrona now rears its roofs: charming and baroque, but definitely less grand and much more recent. Copenhagen is Mycenae, while Ogygia, the island where the nymph Calpyso held Ulysses captive for seven years, is one of the Faroe Islands.
The cyclopes lived in Norway’s Tosenfjorden. Hades, the pagan Greek underworld, was in Russian Karelia. And Ithaca, the mythical home of Ulysses, is the tiny and otherwise rather unremarkable Danish island of Lyø.
The underworld — in Russian Karelia
Vinci spins a fantastic tale, but does any of it hold water? There is very little archaeological evidence of a highly developed Bronze Age civilization in the Baltic region during the time that would fit his story. And the evidence he presents is cherry-picked, often ignoring clues to the contrary. In the words of one critic, Vinci “uses faint indicators to draw enormous conclusions, and hides or is blind to contradicting evidence,” in the manner of many popular books about UFOs, mermaids, or Atlantis.Still, Vinci is not alone. The identity of Ithaca, so vaguely described by Homer, continues to exercise writers and historians. Some examples from recent centuries:
- The 19th-century Belgian amateur historian Théophile Cailleux placed the scenes of Homer’s epic on the European shores of the North Atlantic, but farther south than Vinci: Troy near Cambridge in England and Ithaca near Cadiz in southwest Spain.
- Around that same time, the English novelist Samuel Butler hypothesized the Odyssey was written by a Sicilian woman (who inserted herself into the work as Nausicaa, the young daughter of King Alcinous), and that the setting of the epic is Sicily itself.
- The Greek historian Manolis Koutlis, to name a last but by no means final example, identified Ithaca as Faial, one of the Azores islands in the middle of the Atlantic Ocean.
