I am sure my governor reads shit like this and passes out from all the blood rushing into his dick. They've already refused to reopen schools or have sportzball until muh vaccine is found. If he could figure out how to be Victoria, he would do this too.wtf I love America now
Navigation
Install the app
How to install the app on iOS
Follow along with the video below to see how to install our site as a web app on your home screen.
Note: This feature may not be available in some browsers.
More options
Style variation
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Wuhan Coronavirus: Megathread - Got too big
- Thread starter JosephStalin
- Start date
- Status
- Not open for further replies.
- Joined
- Jul 1, 2017
It's a mechanism to destroy individualism and spread a Chinese sort of collectivism into Western society and encourage more trust and dependence on the government and the "experts". An individualist society like the US and to a lesser degree most all the West before recent years would say your safety from the virus is a personal responsibility and would at most have measures to "flatten the curve". The sick and vulnerable would be quarantined. A collectivist society like China demands everyone do their part for some greater good, which means your freedoms are gone and we can seal you up in your apartment.Maybe this is the alternative plan. In those pod-communities with ever-changing occupants and preferably no walls, just bunk beds, you can't form deep, trusting friendships and you have no privacy and must always expet that a dangerhair snitch will be around to report you. But most people really don't like the idea of cramped pod-communities and all that shit, so now the idea to keep people from getting too close and exchange deep thoughts and ideas (which is doubleplusungood) is to enforce distancing.
Mindbogglingly, the West chose to borrow greatly from the Chinese model. I never in my life would've imagined that except for a truly apocalyptic plague (which this never was, even the earliest reports suggested no more than 4-5% deathrate) something like that would occur in Western countries, let alone a bunch of people on Kiwifarms of all websites praising it and bashing anyone who opposes it as "selfish" like in March or in the Community Watch quarantine. From Day 1, this has been a great social experiment to see how far the world elite can push people into embracing technocratic collectivism.
They can't lose at this point. If the virus magically does end up causing the equivalent of 15 Holocausts globally or however many Dr. Ferguson said it would, then they can say "see, we didn't overreact at all!" If it goes away while barely killing anybody, they can say "thank god the government and enough people listened to our decrees or else way more would've died." Enough people will wholly buy into that narrative and swallow the next crisis narrative they get fed, probably something about taxing meat or cars to save the environment, since 2030 is the last chance to stop global warming before the icecaps inevitably melt and we all die by 2100 or whatever.
Now what's the mark of the beast, a face mask or the vaccine?Yeah but Christians have read Revelation.
- Joined
- Dec 30, 2018
Now what's the mark of the beast, a face mask or the vaccine?
The mobile phone you carry.
Meriasek
kiwifarms.net
- Joined
- May 16, 2020
Yeah, there is a definitely a sort of collectivist note to all the propaganda. All "We can do it", "Together we are strong", that kind of stuff. All aimed at making the collective more important than the individual.It's a mechanism to destroy individualism and spread a Chinese sort of collectivism into Western society and encourage more trust and dependence on the government and the "experts".
However, I think the public's opinion on experts has changed quite a bit after the initial confusion, because, well, people realized that experts are not always all-knowing and science isn't always 100% reliable from the start.
Funny enough, the only expert Germany's MSM accepted, a virologist who became a bit of a shooting star during the Holocoof (despite being dead wrong about SARS 1 or the swine flu, I don't remember which one), is now saying that quarantine should be just five days because otherwise it would just be a factual continuous lockdown, tests should only be done after the quarantine, and reinfection is not an issue. Also, our minister of health said that given what we know now, closing down shops and barbers in March was unnecessary, and there will be no further limits on contacts with the elderly in care facilities.
So maybe there will actually be some humility among our politicians?
- Joined
- May 17, 2019
At this point, all Trump needs to do to be re-elected is say, “If I get back in office I’ll be able to work on reopening the country.”
Because a lot of people are getting pretty sick of this shit.
Because a lot of people are getting pretty sick of this shit.
Sekirodiealot
kiwifarms.net
- Joined
- Dec 18, 2019
I'm still not convinced with this lasting forever.
Standardized Profile
kiwifarms.net
- Joined
- Oct 5, 2018
Politics attracts people who like manipulating and controlling others, and it promotes people who are good at those things. It is inevitable that at least some politicians will carry these tendencies as far as they can, and they will do so skillfully. They do this for the satisfaction they derive from manipulation and the exercise of power, not in pursuit of any particular scheme or agenda.In principle it's fine, but in the current situation it seems rather dangerous.
Homegrown Homophobia
kiwifarms.net
- Joined
- May 17, 2017
I think at least for the US the debacle over Pelosi getting her hair cut is going to be a turning point for this lockdown bullshit, plus the coming Trump victory in Novevmber.
- Joined
- Feb 24, 2016
Too bad no one will ask her the real tough questions: "As someone who is 80, are you taking hydroxychloroquine as a prophylactic? Or is the pandemic not as bad as it has made out to be?"I think at least for the US the debacle over Pelosi getting her hair cut is going to be a turning point for this lockdown bullshit, plus the coming Trump victory in Novevmber.
- Joined
- Dec 9, 2015
I'm positive that a worse tax season than usual will give "experts" and governors some pause over their "righteous" cause.I'm still not convinced with this lasting forever.
Once they realize that their actions could come back to bite them in the ass, I think there'll be more calls to reopen shit.
Sekirodiealot
kiwifarms.net
- Joined
- Dec 18, 2019
That's what I'm thinking. I'm just not too big on this defeatist attitude going on here. They'll think twice about reacting this way in the future. It makes me wonder what movies based around this would be likeI'm positive that a worse tax season than usual will give "experts" and governors some pause over their "righteous" cause.
Once they realize that their actions could come back to bite them in the ass, I think there'll be more calls to reopen shit.
I imagine a lot of the cancer will be chemoed out Nov 3rd. 






ChikN10der
kiwifarms.net
- Joined
- Aug 12, 2020
You never know. The weirdest things end up being the last straw sometimes.I think at least for the US the debacle over Pelosi getting her hair cut is going to be a turning point for this lockdown bullshit, plus the coming Trump victory in Novevmber.
- Joined
- Mar 1, 2020
Just as I thought, COVID-19 can be defeated by the humble Vitamin D. The people who are dying from it unwittingly have chronic hypovitaminosis D.
Take what the guy in that first blog article said, about how he was leery about Vitamin D in excess because too much of it up-regulates ACE2 and increases risk of infection. This may be true, but at the same time, ACE2 converts the inflammatory Ang II into Ang 1-7, reducing AT1R activity and the associated inflammation. ACE2 also inactivates bradykinin. Also, having high Vitamin D levels moderates cytokine activity and reduces oxidative stress by moderating the enzymes that produce reactive oxygen species.
Basically, having sufficient Vitamin D levels keeps one from experiencing the oxidative and inflammatory cascade characteristic of the severe injuries from a COVID-19 infection.
In summary, we must give Corona-chan the D.
It has been proposed that the activation of the vitamin D receptor (VDR) signaling pathway may generate beneficial effects in ARDS [11] by decreasing the cytokine/chemokine storm, regulating the renin‑angiotensin system, modulating neutrophil activity and by maintaining the integrity of the pulmonary epithelial barrier, stimulating epithelial repair and tapering down the increased coagulability [12,13,14,15,16]. Recently, two ecological studies have reported inverse correlations between national estimates of vitamin D status and the incidence and mortality of IDOC-19 in European countries [17,18]; lower concentrations of circulating 25 (OH) D have also been reported to be associated with susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection [19] and the severity of the evolution of COVID-19 [20]. Vitamin D deficiency is frequent in wintertime even in Southern Spain [21] and even more so in patients requiring ICU treatment [22].
Take what the guy in that first blog article said, about how he was leery about Vitamin D in excess because too much of it up-regulates ACE2 and increases risk of infection. This may be true, but at the same time, ACE2 converts the inflammatory Ang II into Ang 1-7, reducing AT1R activity and the associated inflammation. ACE2 also inactivates bradykinin. Also, having high Vitamin D levels moderates cytokine activity and reduces oxidative stress by moderating the enzymes that produce reactive oxygen species.
Basically, having sufficient Vitamin D levels keeps one from experiencing the oxidative and inflammatory cascade characteristic of the severe injuries from a COVID-19 infection.
In summary, we must give Corona-chan the D.

- Joined
- Jan 6, 2019
Just as I thought, COVID-19 can be defeated by the humble Vitamin D. The people who are dying from it unwittingly have chronic hypovitaminosis D.
Take what the guy in that first blog article said, about how he was leery about Vitamin D in excess because too much of it up-regulates ACE2 and increases risk of infection. This may be true, but at the same time, ACE2 converts the inflammatory Ang II into Ang 1-7, reducing AT1R activity and the associated inflammation. ACE2 also inactivates bradykinin. Also, having high Vitamin D levels moderates cytokine activity and reduces oxidative stress by moderating the enzymes that produce reactive oxygen species.
Basically, having sufficient Vitamin D levels keeps one from experiencing the oxidative and inflammatory cascade characteristic of the severe injuries from a COVID-19 infection.
In summary, we must give Corona-chan the D.
is that why you haven't gotten it yet? because of all the salty futa D you've been enjoying?
- Joined
- Oct 21, 2019
Tyrant Timmy Walz dared to tweet out the Suicide Prevention Awareness Month info after telling us all to prepare for a cold, dark winter yesterday.
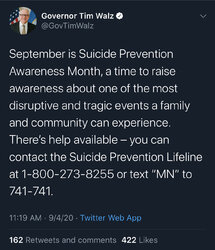
The replies were predictably upset about his tone-deafness. This level of pushback is notable from a culture of passive aggressiveness.

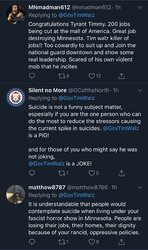
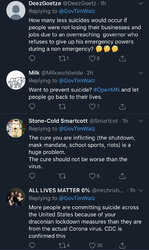

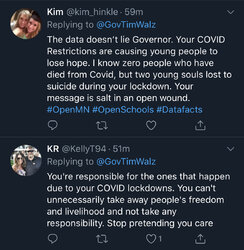
One guy with TDS would rather believe that everyone expressing opposition to the lockdowns is a bot.
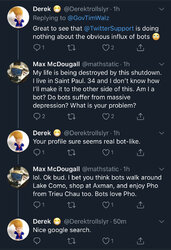

The replies were predictably upset about his tone-deafness. This level of pushback is notable from a culture of passive aggressiveness.





One guy with TDS would rather believe that everyone expressing opposition to the lockdowns is a bot.

- Joined
- Dec 18, 2019
Why do people put up with this? We're talking about riots in America over much less...In Melbourne, right now, the people are under a strict curfew that starts at 8PM. The cops have set up roadblocks around the city and you require special permits to travel 5km from your home. You must produce your papers when asked. Folks have to stay inside 23 hours a day, they're allowed out for 1 hours exercise (just like a Federal pen). Face masks are of course mandatory at all times, even when outside. The cops can issue spot fines for infringements of up to $20,000. Anyone who complains on social media is being closely monitored and the police have made it clear they'll be paying visits to people who get too mouthy about the lockdown. All businesses, except essential services are closed (and pretty much have been since March). All schools and universities are closed. This hard lockdown started 4 weeks ago as the government lost control of it's quarantine facilities, having staffed them with immigrant day workers (I shit you not).
- Joined
- Jul 7, 2020
Has anyone tried to get a doctors note exempting themselves from the masks? I'm planning on going to ask for one soon. They cause me so much anxiety and I can't concentrate on anything with them on.
Wow, are you really such a pussy? I used to live in a place where the air pollution was intense and I would take 2 hour walks wearing a mask. The kind of mask with a valve, not a flimsy surgical mask. People even work out in these masks, but they cause you anxiety? Maybe you should just stay at home because it seems like life is just too much for you to handle.
Mind you I'm not taking a stance right now on the issue of whether mask mandates are appropriate. I'm just saying you sound like a whiny child and you maybe ought to harden the fuck up.
- Joined
- Mar 1, 2020
is that why you haven't gotten it yet? because of all the salty futa D you've been enjoying?
42% of Americans are Vitamin D deficient. It varies highly by race. 60% of Hispanics and 80% of African-Americans have a Vitamin D deficiency. Higher melanin content means less UV light forming cholecalciferol in the skin.
Now, consider the huge race gaps in COVID-19 morbidity and mortality.
These disparities can be observed at all ages, but are especially marked in somewhat younger age groups. These disparities can be seen more clearly by comparing the ratio of death rates among Black and Hispanic/Latino people to the rate for white people in each age category. Among those aged 45-54, for example, Black and Hispanic/Latino death rates are at least six times higher than for whites.
Observe how the media has consistently reported that “systemic inequality” has led to different outcomes and delayed treatment for these patients. The press will say anything to avoid the politically incorrect conclusion that intrinsic biological differences are to blame. In fact, they’ll even say things like, oh, “Black people are dying of Corona because they live in Cancer Alley!”
So, not only are they being disingenuous and divisive by promoting a myth of class-driven inequality in COVID-19 medical outcomes, they are actually endangering people’s lives by failing to inform them about an easily corrected nutritional deficiency. This is so Big Pharma can sell people $3,100 courses of Remdesivir and give them kidney failure, instead of people buying a $13 bottle of Vitamin D caplets from their grocery store.
I smell scandal for miles.
- Joined
- Dec 18, 2019
......... so bots can reflexively google search in response to random tweets now.One guy with TDS would rather believe that everyone expressing opposition to the lockdowns is a bot.
View attachment 1572049
Edit: spelling
Last edited:
- Status
- Not open for further replies.